Struggling to Breathe: A Guide to Respiratory Health
Breathing is one of the most fundamental processes of life, yet it’s something most of us take for granted—until we struggle to do it. When we face issues with our ability to breathe, it can be alarming and disruptive to our daily lives. This guide, titled “Struggling to Breathe: A Guide to Respiratory Health,” aims to provide you with valuable insights into the causes, symptoms, and management of respiratory problems, empowering you to take control of your respiratory health.
Table of Contents
Understanding Respiratory Health
Respiratory health refers to the efficiency and effectiveness of the organs and tissues involved in breathing. The lungs, airways, and muscles work together to deliver oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide from the body. When any part of this system is compromised, it can lead to breathing difficulties, making you feel like you’re constantly “struggling to breathe.”
Common Respiratory Problems
- Asthma: One of the most prevalent respiratory conditions, asthma causes the airways to become inflamed and narrowed, leading to wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Individuals with asthma often describe the sensation of “struggling to breathe,” especially during an asthma attack.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): This group of diseases, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis, causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. People with COPD experience ongoing symptoms that make them feel like they are “struggling to breathe” every day, particularly during physical activity or when exposed to irritants.
- Allergies: Allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander can trigger allergic reactions, leading to respiratory symptoms such as sneezing, coughing, and a feeling of breathlessness. For some, seasonal changes can be a time of “struggling to breathe.”
- Pneumonia: A severe lung infection, pneumonia causes the air sacs in the lungs to fill with fluid or pus, leading to coughing, fever, and difficulty breathing. In severe cases, patients may feel like they are “struggling to breathe,” requiring immediate medical attention.
- Anxiety and Panic Attacks: Anxiety disorders can manifest physically, with symptoms including rapid breathing or hyperventilation. During a panic attack, the sensation of “struggling to breathe” can be overwhelming, even though there is no physical obstruction to airflow.

Causes of Breathing Difficulties
The causes of breathing difficulties are diverse and can be linked to environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and underlying health conditions. Some common causes include:
- Smoking: Smoking is a leading cause of respiratory diseases such as COPD and lung cancer. The damage to lung tissue caused by smoking can leave individuals constantly “struggling to breathe.”
- Air Pollution: Exposure to pollutants in the air, such as smog, chemicals, and particulate matter, can irritate the airways and exacerbate conditions like asthma and COPD, leading to a persistent feeling of “struggling to breathe.”
- Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, can restrict the movement of the diaphragm and reduce lung capacity, making it more difficult to breathe comfortably.
- Infections: Respiratory infections, such as the flu or COVID-19, can cause inflammation in the airways and lungs, leading to symptoms of breathlessness. In severe cases, individuals may feel as if they are “struggling to breathe” with every breath they take.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of respiratory issues is crucial for early intervention and treatment. Some common signs that you may be “struggling to breathe” include:
- Shortness of Breath: Feeling like you can’t catch your breath, especially during physical activity or when lying down, is a clear indicator of respiratory distress.
- Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling sound when breathing can signal that your airways are narrowed, making it harder for air to flow in and out of your lungs.
- Chronic Cough: A persistent cough that doesn’t go away, especially if it produces mucus, can be a sign that your respiratory system is under stress.
- Chest Tightness: The sensation of tightness or pressure in the chest, particularly during exertion, can indicate that your lungs are not getting enough air.
- Fatigue: When your body is “struggling to breathe,” it may not be getting the oxygen it needs, leading to feelings of exhaustion and weakness.
Managing Respiratory Health
Taking steps to improve and manage your respiratory health can reduce the frequency and severity of episodes where you feel like you’re “struggling to breathe.” Here are some strategies to consider:
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, quitting is the single most important step you can take to improve your respiratory health. Over time, your lungs will begin to heal, and you will find it easier to breathe.
- Avoid Triggers: If you have asthma or allergies, identifying and avoiding your triggers—such as pollen, smoke, or certain foods—can help prevent symptoms. Using air purifiers and regularly cleaning your living space can reduce exposure to indoor allergens.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity strengthens the muscles involved in breathing, improves lung capacity, and boosts overall health. Start with low-impact exercises like walking or swimming, and gradually increase intensity as your fitness improves.
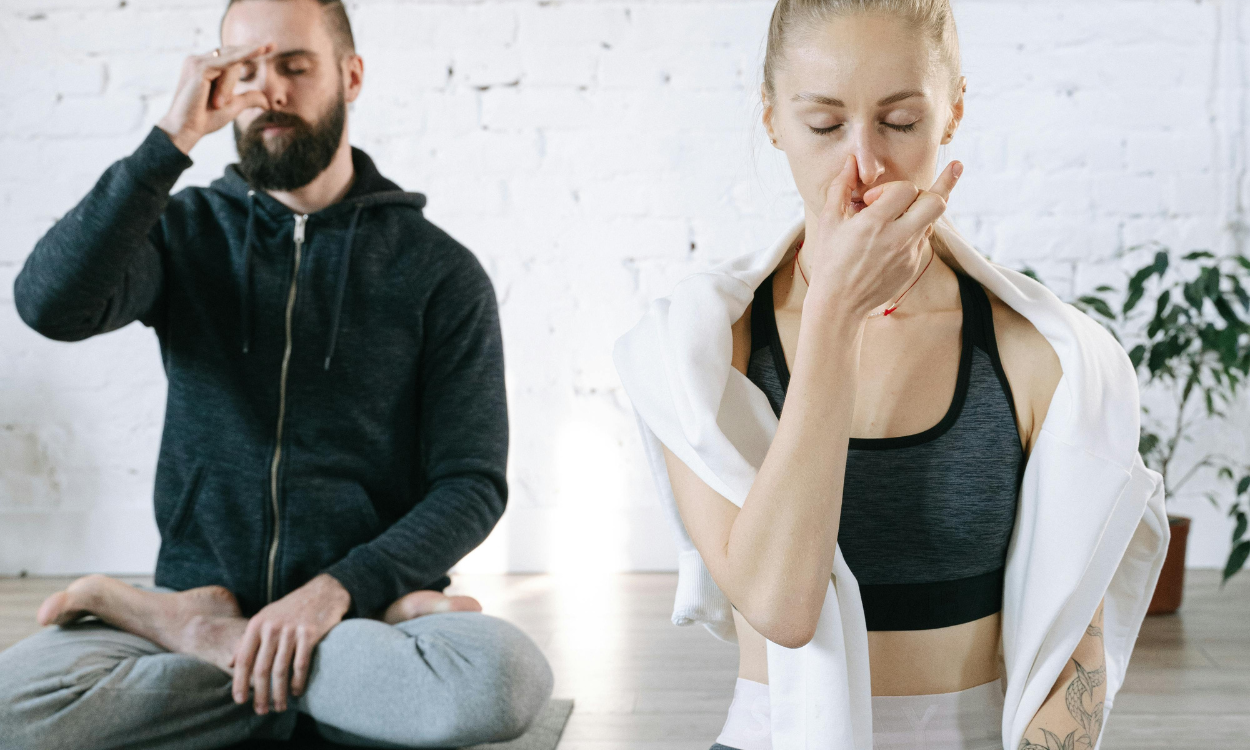
- Practice Breathing Exercises: Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing and pursed-lip breathing can help you manage shortness of breath by promoting relaxation and improving oxygen exchange.
- Medication and Inhalers: For chronic conditions like asthma or COPD, using prescribed medications and inhalers as directed by your healthcare provider can keep symptoms under control and reduce the sensation of “struggling to breathe.”
- Monitor Air Quality: Stay informed about local air quality levels and try to stay indoors on days when pollution levels are high. Using an air conditioner or air purifier can help maintain clean indoor air.
- Seek Medical Advice: If you frequently find yourself “struggling to breathe,” it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. They can perform tests to diagnose any underlying conditions and recommend appropriate treatments.
When to Seek Emergency Help
Sometimes, breathing difficulties can be a sign of a life-threatening condition. Seek emergency medical help if you experience:
- Severe shortness of breath that comes on suddenly or worsens rapidly
- Chest pain that spreads to your arm, neck, or jaw
- Bluish lips or face, indicating a lack of oxygen
- Confusion or fainting
These symptoms may indicate a heart attack, severe asthma attack, or other serious conditions requiring immediate intervention.
Conclusion
“Struggling to Breathe: A Guide to Respiratory Health” is intended to help you understand the importance of respiratory health and provide practical advice on managing and improving your breathing. By taking proactive steps to care for your lungs and seeking medical advice when necessary, you can reduce the frequency of breathlessness and enjoy a fuller, healthier life. Remember, every breath counts, so don’t hesitate to take action if you find yourself struggling to breathe.