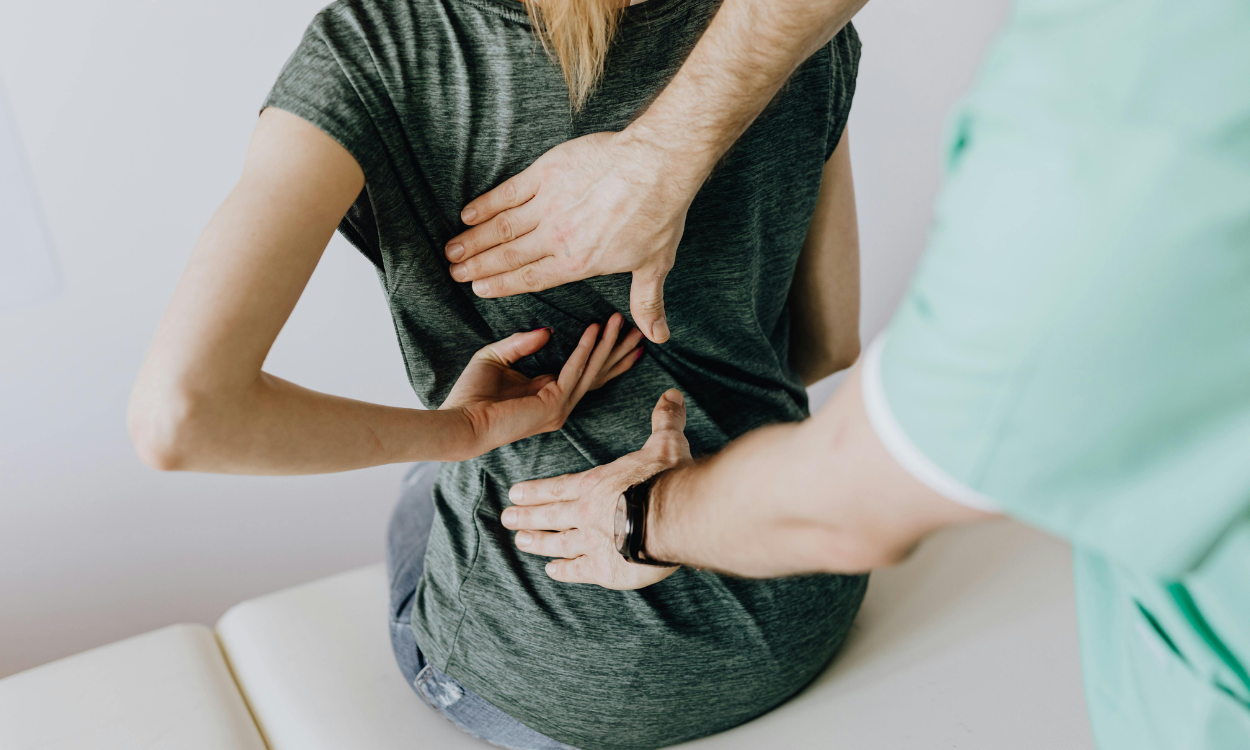
Back pain is a common ailment that affects millions of people worldwide, impacting daily life, work productivity, and overall well-being. Whether it’s a dull ache or a sharp, debilitating pain, back pain can stem from various causes and require different treatment approaches. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, prevention strategies, and care options for back pain, offering practical advice to help you manage and alleviate discomfort.
Table of Contents
Understanding Back Pain
Back pain can occur anywhere along the spine, from the neck to the lower back. It can be categorized into different types based on its duration and severity:
- Acute Back Pain: This type lasts for a short period, usually a few days to a few weeks. It often results from muscle strain, ligament sprains, or minor injuries.
- Chronic Back Pain: This pain persists for more than three months and can be continuous or intermittent. Chronic back pain may result from underlying medical conditions, such as arthritis, herniated discs, or spinal stenosis.
- Neuropathic Pain: Caused by nerve damage or irritation, this type of pain can lead to tingling, numbness, or a burning sensation.

Common Causes of Back Pain
Understanding the causes of back pain is crucial for effective prevention and care. Some common causes include:
- Muscle Strain and Ligament Sprain: Lifting heavy objects, sudden movements, or poor posture can strain muscles and sprain ligaments, leading to back pain.
- Herniated Discs: When the soft material inside a disc bulges or ruptures, it can press on nerves, causing pain.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: As we age, the discs between our vertebrae can wear down, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis can affect the spine, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
- Scoliosis: An abnormal curvature of the spine can lead to chronic back pain.
- Osteoporosis: Weakening bones can cause vertebral fractures, resulting in pain.
- Infections and Tumors: Though less common, infections and tumors can cause back pain.
Symptoms of Back Pain
Back pain can manifest in various ways, depending on the underlying cause and location. Common symptoms include:
- Dull or Aching Pain: A general discomfort that may worsen with movement or certain activities.
- Sharp or Stabbing Pain: Intense pain that can make movement difficult.
- Radiating Pain: Pain that spreads to other areas, such as the legs or arms, often associated with nerve involvement.
- Muscle Spasms: Involuntary muscle contractions that can cause pain and stiffness.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty moving or bending due to pain and stiffness.
Prevention Strategies for Back Pain
Preventing back pain involves adopting healthy habits and lifestyle changes. Here are some effective strategies:
- Maintain Proper Posture: Good posture reduces strain on the spine. Sit and stand with your back straight and shoulders relaxed. Use ergonomic furniture and supportive shoes.
- Exercise Regularly: Strengthening the muscles around your spine can prevent injuries. Focus on core-strengthening exercises, stretching, and aerobic activities like walking or swimming.
- Lift Properly: When lifting heavy objects, use your legs, not your back. Bend at the knees and keep the object close to your body.
- Stay Active: Avoid prolonged periods of sitting or standing. Take breaks to move around and stretch.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can strain your back, so maintaining a healthy weight is crucial.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can reduce blood flow to the spine, increasing the risk of disc degeneration.
- Use Proper Sleeping Positions: Sleep on a supportive mattress and use pillows to maintain proper spinal alignment.

Care and Treatment Options for Back Pain
If you’re experiencing back pain, several treatment options can help alleviate discomfort and promote healing. These include:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen your back and improve flexibility.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractors use spinal manipulation to relieve pain and improve function.
- Massage Therapy: Massage can relax tight muscles and improve blood flow to the affected area.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs can reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese therapy involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to relieve pain.
- Prescription Medications: For severe pain, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications, such as muscle relaxants or opioids.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and relieve pain in specific areas.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to address structural issues or nerve compression.
When to See a Doctor
While most back pain resolves with self-care and home treatments, some situations require medical attention. Seek professional help if you experience:
- Severe or Worsening Pain: Pain that doesn’t improve with rest or worsens over time.
- Numbness or Tingling: Especially if it affects your legs or arms.
- Loss of Bladder or Bowel Control: This may indicate a serious condition called cauda equina syndrome.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Along with back pain, this could signal an underlying health issue.
- Fever: Accompanied by back pain, it may indicate an infection.